| |
|
|
|
 Structural and Functional Analysis of Proteins with Pharmacological or Biotechnological Significance Structural and Functional Analysis of Proteins with Pharmacological or Biotechnological Significance
|
|
(A) Trichosanthin, a Chinese Medicinal Protein with Multiple Pharmacological Properties
|
|
Trichosanthin (TCS) is a ribosome-inactivating protein isolated from the root tuber of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. It is used to induce abortion in China and has been found to have anti-tumour and anti-HIV effects. We have previously cloned the cDNA of TCS, developed a method to purify the recombinant TCS in Escherichia coli, found the epitopes of TCS by mapping with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies and generated TCS derivatives with reduced antigenicity lengthened half-life in vivo. Our present focus is on: (1) mammalian proteins that interact with TCS, (2) structure-function study of other unique ribosome-inactivating proteins, including maize ribosome-inactivating protein and Shiga toxin and (3) improving the efficacy of these proteins for killing HIV-infected cells.
|
|
 Recent Publications: Recent Publications:
|
- Lee, K.M., Yu, C.W., Chiu, T.Y., Sze, K.H., Shaw, P.C. and Wong, K.B. (2012) Solution structure of the dimerization domain of the eukaryotic stalk P1/P2 complex reveals the structural organization of eukaryotic stalk complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 40: 3172-3182.
- Ng, Y.M., Yang, Y.H., Sze, K.H., Zhang, X., Zheng, Y.T. and Shaw, P.C. (2011) Structural characterization and anti-HIV-1 activities of arginine/glutamate-rich polypeptide luffin P1 from the seeds of sponge gourd (Luffa cylindrical). J. Str. Biol. 174: 164-172.
- Law, S.K.Y., Wang, R.R., Mak, A.N.S., Wong, K.B., Zheng, Y.T. and Shaw, P.C. (2010) A switch-on mechanism to activate maize ribosome-inactivating protein for targeting HIV-infected cells. Nucl. Acids Res. 38: 6803-6812.
- Lee, K.M., Yu, C.W., Chan, D.S., Chiu, T.Y., Zhu, G., Sze, K.H., Shaw, P.C. and Wong, K.B. (2010) Solution structure of the dimerization domain of ribosomal protein P2 provides insights for the structural organization of eukaryotic stalk. Nucl. Acids Res. 38: 5206-5216.
- Yang, Y., Mak, A.N., Shaw, P.C. and Sze, K.H. (2009) Solution structure of an active mutant of maize ribosome-inactivating protein (MOD) and its interactiion with the ribosomal stalk protein P2. J. Mol. Biol. 395: 897-907
- Too, P.H.M., Ma, M.K.W., Mak, A.N.S.,
Wong, Y.T., Tung, C.K.C., Zhu, G., Au, S.W.N., Wong, K.B. and Shaw,
P.C. (2009) The C-terminal fragment of the ribosomal P
protein complexed to trichosanthin reveals the interaction
between the ribosome-inactivating protein and the
ribosome. Nucl. Acids Res. 37: 602-610.
- Yang, Y., Mak, A.N.S., Shaw,
P.C. and Sze, K.H. (2008) 1H, 13C and 15N backbone and side chain
resonance assignments of a 28 kDa active mutant of maize ribosome-inactivating
protein (MOD). Biomol. NMR Assign. 1: 187-189.
- Juri Ayub, M., Ma K.W., Shaw,
P.C. and Wong, K.B. (2007) Trypanosoma cruzi: High ribosomal resistance
to trichosanthin inactivation. Exp. Parasitol. 118: 442-447.
- Mak, A.N.S., Wong, Y.T., An, Y.J., Cha,
S.S., Sze, K.H., Au, S.W.N., Wong, K.B. and Shaw,
P.C. (2007) Structure-function study of maize ribosome-inactivating
protein: implications for the internal inactivation region and the sole
glutamate in the active site. Nucl. Acids Res. 35: 6259-6267.
- Chan, S.B., Chu, L.O., Lee, K.M., Too, H.M.,
Sze, K.H., Zhu, G., Shaw, P.C. and Wong, K.B.
(2007) Interaction between trichosanthin, a ribosome-inactivating protein,
and the ribosomal stalk protein P2 by chemical shift perturbation and mutagenesis
analysis. Nucl. Acids Res. 35: 1660-1672.
|
|
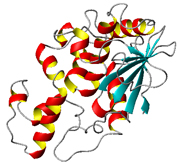
Crystal Structures of (I) Active Form and (II) Inactive Form of Maize Ribosome-Inactivating Protein |
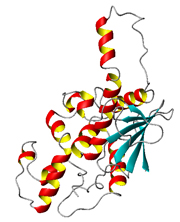
Crystal Structure of the Trichosanthin-Ribosomal P Protein Complex |
 |
|
|
I |
II |
|
|
(B) Structure-Function Study of Influenza Virus Proteins
|
|
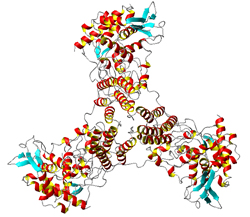
Influenza is a contagious respiratory illness causing annual epidemics and occasional pandemics. The death toll of influenza epidemics worldwide is in the range of 250,000 to 500,000 each year. Since the 1997 outbreak of influenza A strain H5N1 in Hong Kong, avian flu has become the major threat for the next pandemic. The genome of influenza A virus comprises eight segments of RNA encoding 11 identified polypeptides. Recently, our group has solved the crystal structure of H5N1 nucleoprotein. We are now working on: (1) How nucleoprotein binds RNA and forms polymers, (2) how nucleoprotein is transported inside cell, (3) Why the non-structural protein is the key protein for pathogenicity.
|
|
 Recent Publications: Recent Publications:
|
|
- Ng, A.K., Chan, W.H., Choi, S.T., Lam, M.K., Lau, K.F., Chan, P.K., Au, S.W., Fodor, E. and Shaw, P.C. (2012) Influenza polymerase activity correlates with the strength of interaction between nucleoprotein and PB2 through the host-specific residue K/E627. PLoS One. 7(5):e36415.
- Ng, A.K., Lam, M.K., Zhang, H., Liu, J., Au, S.W., Chan, P.K., Wang, J. and Shaw, P.C. (2012) Structural basis for RNA binding and homo-oligomer formation by influenza B virus nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 86: 6758-67.
- Vreede, F.T., Ng, A.K., Shaw, P.C. and Fodor, E. (2011) Stabilization of influenza virus replication intermediates is dependent on the RNA-binding but not the homo-oligomerization activity of the viral nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 85: 12073-12078.
- Chan, W.H., Ng, A.K., Robb, N.C., Lam, M.K., Chan, P.K., Au, S.W., Wang, J.H., Fodor, E. and Shaw, P.C. (2010) Functional analysis of influenza H5N1 nucleoprotein tail loop reveals amino acids that are crucial for oligomerization and ribonucleoprotein activities. J. Virol. 84: 7337-7345.
- Ng, A.K.L., Wang, J.H. and Shaw, P.C. (2009) Structure and sequence analysis of influenza A virus nucleoprotein. Sci. China C. Life Sci. 52: 439-449.
- Gao, G.F. and Shaw, P.C. (2009) The challenges of avian influenza virus: mechanism, epidemiology and control. (Editorial). Sci. China C. Life Sci. 52: 405-406.
- Ng, A.K.L., Zhang, H., Tan, K., Li, Z.,
Liu, J.H., Chan, P.K.S., Li, S.M., Chan, W.Y., Au, S.W.N.,
Joachimiak, A., Walz, T., Wang, J. and Shaw, P.C. (2008)
Structure of the influenza virus A H5N1 nucleoprotein: implications
for RNA binding, oligomerization and vaccine design. FASEB J. 22: 3638-3647.
|
|
Crystal Structure of H5N1 Nucleoprotein
|
|
|

|
|
|
| |
|
|
|