Main Next
1. Sequence similarity
search using BLAST
query sequence:
APVKSQESIN QKLALVIKSG KYTLGYKSTV KSLRQGKSKL IIIAANTPVL
RKSELEYYAM LSKTKVYYFQ GGNNELGTAV GKLFRVGVVS ILEAGDSDIL
TTLA
The first thing you might want to do is to search if there is any similar
sequences in the databases. One of the database searching program available
on the web is BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool).
1. Go to the BLAST home page at the National Center for Biotechnology Information
(NCBI):
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/
2. Choose "Basic BLAST search".
3. Select which program to use. Since we are searching protein sequence,
we select the 'blastp' program:
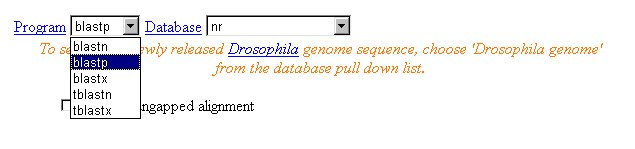
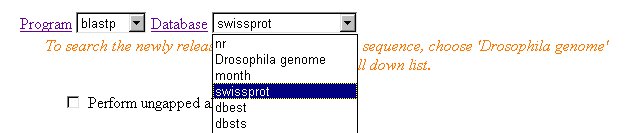
4. Select database. Two commonly used databases for protein sequence searching:
-
swissprot - SWISS-PROT
is a high quality protein sequence database with excellent annotations.
Minimal redundancy but poorer sequence coverage.
-
nr - Non-Redundant database. It is a composite protein sequence
database consisted of non-identical sequences derived from several databases:
GenPept, PDB, Swiss-Prot, PIR, PRT. Although its name is called 'non-redundant',
it may contain redundant sequences as a result of polymorphisms, sequencing
errors and sequences of protein fragment. Comprehensive sequence coverage
but poorer quality of the database.
We will use swissprot in this example:
5. Copy the query sequence and paste it into the window:
APVKSQESIN QKLALVIKSG KYTLGYKSTV KSLRQGKSKL IIIAANTPVL
RKSELEYYAM LSKTKVYYFQ GGNNELGTAV GKLFRVGVVS ILEAGDSDIL
TTLA

Then press the 'Search' button.
6. You will receive a notification saying your search has been submitted
and put into a queue. Press the 'Format results' button to check your results.
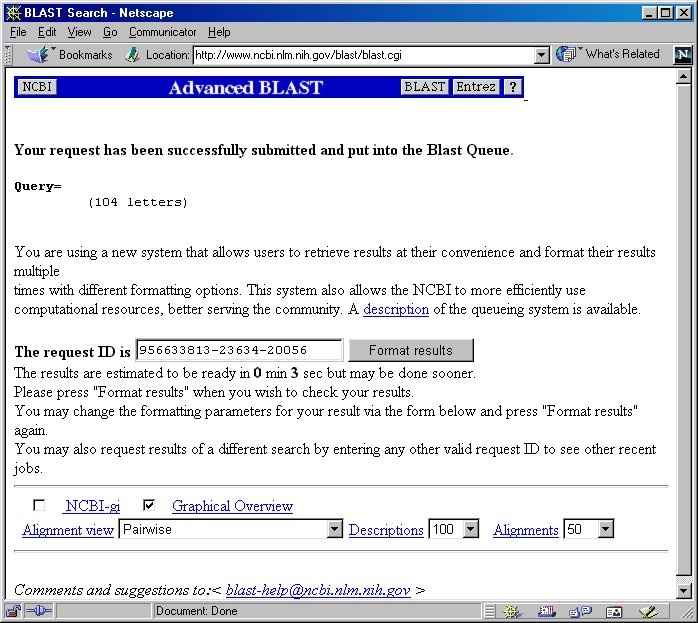
7. You should now see a new window of your BLAST search results. Scroll
down the window until you see the following:
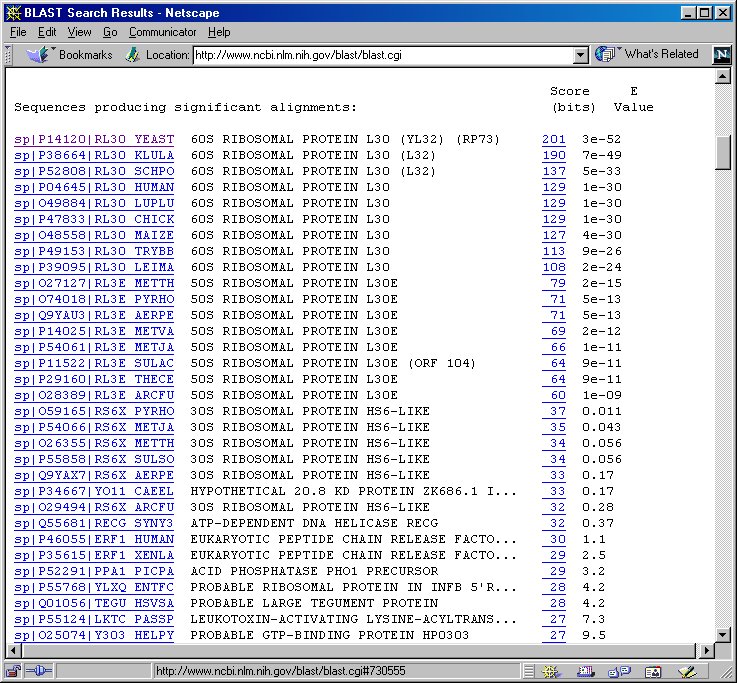
8. Check if the matches are significant or not.
The BLAST results report a list of sequences that may be
similar to your query sequence. The statistical significance of the matches
is measured by E-value (Expect
value). Highly significant matches should have E-values very close
to zero.
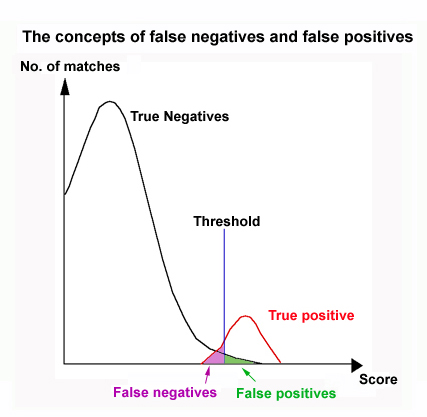 By default, BLAST reports all sequences that have an E-value <= 10.
By default, BLAST reports all sequences that have an E-value <= 10.
9. Firstly, we use a conservative threshold E-value. Take a look at the
proteins with E-value < 0.001. What generalization can you make?
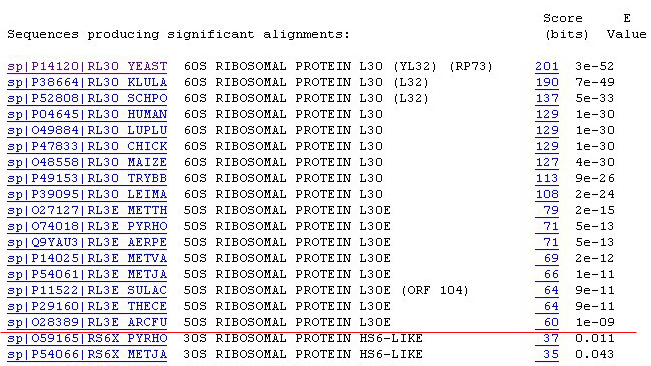
10. We can obtain more information about the matches by clicking on the
bits score. Try click on the highest bits score '201':

Notice the query sequence exactly matched (identities=100%) the sequence
of RL30_YEAST. What does it tell you about the query sequence?
11. Now look at sequences that have E-values > 0.001. The next several
matches are HS6-like ribsosomal proteins. The ribsomoal protein L30 may
be also related to the ribosomal protein S6.
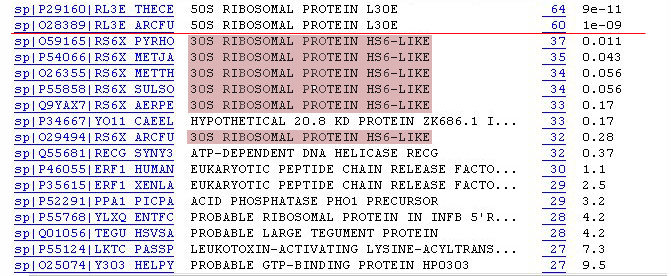
12. A summary of what you have found for your query sequence:
-
It is the yeast ribosomal protein L30.
-
Ribosomal protein L30 is conserved among different organisms.
-
Ribosomal protein L30 may be related to ribosomal protein S6.
Main Next









