Base-pairing in DNA
(Download basepair.pdb)
The following skill will be taught here:
- Identification of bases in DNA
- Display the hydrogen bond pattern
- Measuring the distance between two atoms
Open the file basepair.pdb:
The structure represents a short fragment of DNA consisting of 2 base-
pairs. One of them is an A-T pair and the other one is a G-C pair.
To identify which is which, we can following the following steps:
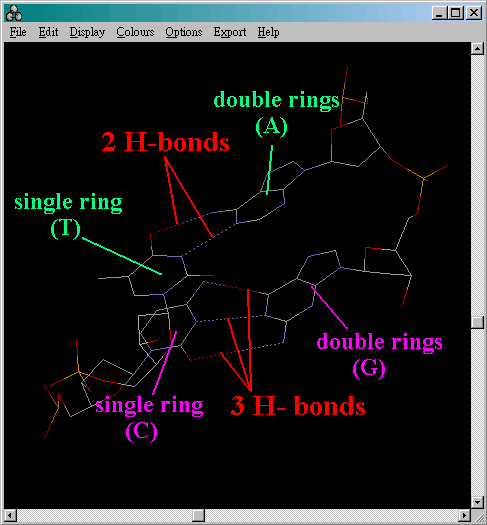
- First of all, identify which is a purine (A or G) - double
rings, and which is a pyrimidines (C or T, NEVER find U in DNA!)- single
ring.
- As we know, there are 2 hydrogen
bonds in A-T bond and 3 hydrogen bonds
in G-C bond. Bear this in mind because we will use this fact in the identification
process.
- Activate the command line interface of RasMol by clicking the "RasMol
Command Line Button" on the Toolbar:
- The command line interface allows you to access the more advanced
features of RasMol. One of them is to show hydrogen bonding pattern. Try to
type the following command in the command window:
RasMol>hbond on
- The dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds between the bases. So we
can have the following predictions:
- If you want to turn off the hydrogen bond display, just type the following
in the command window:
RasMol>hbond off
Measuring the distance between two
atoms
To turn on distance monitor:
RasMol>set picking monitor
Then pick any two atoms in the Main
Window of RasMol:
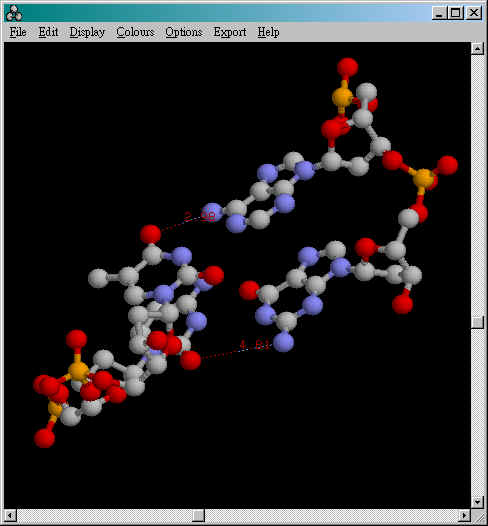
The distance's unit is Angstrom (1 Angstrom= 0.1nm)
To turn off the distance monitor and set the picking
mode back to default:
RasMol>monitor off
RasMol>set picking ident
¡@





