Work of a restriction enzyme : Introduction
Enzyme plays a fundamental role in genetic engineering. There are 3 different types of commonly used enzymes:
- Restriction enzymes 限制性内切酶 are involved in the cutting of target DNA.
- DNA ligase is responsible for joining two fragments of DNA together.
- DNA polymerase is responsible for the polymerization of DNA bases into a DNA strand.
Restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases), being naturally produced in most bacteria, some viruses and eukaryotes, are able to cut DNA fragments at specific DNA sequences.
Restriction enzymes work by hydrolyzing the phosphodiester bond on double stranded DNA and cut the target DNA in two manners that are useful for genetic engineering:
- Blunt end 平整末端: They cut straight across the DNA, leaving no exposed unpaired bases.
For example, SmaI
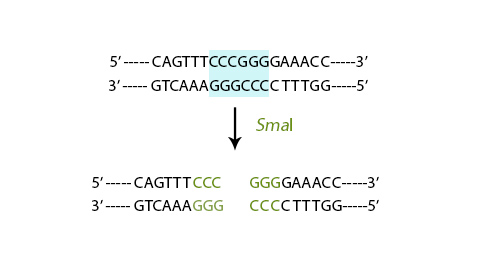
Restriction site is represented by
5’ CCC/GGG 3’
3’ GGG/CCC 5’
where “/” represents cutting point.
- Sticky end 黏性末端: They cut in offset manner, leaving the ends of cut having an overhanging piece of unpaired bases. For example, EcoRI
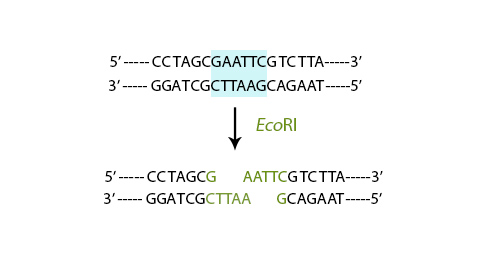
Restriction site is represented by
5’ G/AATT C 3’
3’ C TTAA/G 5’
Any source of DNA treated with same restriction enzyme will produce the same cut.